
Geometry - Introduction
Tutorial
intermediate
+0XP
15 mins
225
Unity Technologies

In this tutorial, we briefly introduce the learning objectives for this project on optimizing Geometry in your mobile 3D application.
Languages available:
1. Overview
It’s very likely that the geometry in your 3D application will represent the vast majority of objects in your 3D mobile application. Geometry will be the most common piece of data that’s processed, so it’s important to give consideration to its implementation and optimization.
This project will highlight optimizations for 3D models that can make a game more efficient while maintaining aesthetic intent, improving the performance and experience on mobile devices.
In this project, you will:
- Explore the fundamental components of geometry and how they contribute to the performance of your game.
- Learn about how implementing models with Level of Detail in mind will improve performance while maintaining object readability.
- Consider other common techniques and best practices that help convey your 3D models’ finer details on a mobile phone’s smaller screen.
2. What is Geometry?
Geometry, or a polygon mesh, is a collection of vertices, edges, and faces that make up the shape of a 3D object. This mesh can be a car, environmental object, character, or any type of asset that appears in a 3D application.
The following image shows the three elements that make up the geometry of a 3D object:
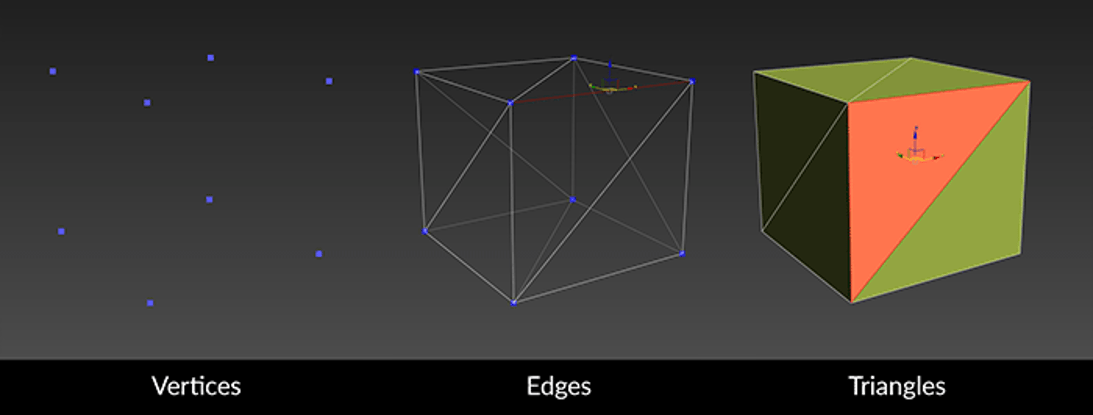
- Vertices are the points that make up the surface of a 3D object.
- Edges connect two vertices with a straight line.
- Triangles consist of three vertices that are connected to each other by three edges. Other terms for a triangle include polygon and face.
(Note: With 3D software like 3ds Max, Maya, or Blender, you often use a four-sided polygon called a quad. Quads can be easier to modify and work with in these 3D programs. When rendered on-screen, all of these polygons are displayed as triangles.)
3. Conclusion
Vertices, edges, and triangles combine to create 3D geometry. Geometry can be as simple as the cube shown above and as complex as a structure composed of thousands of faces. When building a 3D application, it’s important to consider the performance implications of the geometry in your scene. In the next tutorial, we’ll dive into practical methods for optimizing the vertices, edges, and triangles that make up a polygonal mesh.