Optimizing Large-Scale Projects
Tutorial
Beginner
+0XP
10 mins
28
Unity Technologies
Diagnosing and solving optimization issues in a large Scene requires the application of an optimization methodology, as well as a range of skills. This tutorial outlines a process to work through optimization issues in a coherent and structured way. Using this process will provide a consistent framework and approach to optimization that can be adopted across teams and embedded in your general optimization practices.
Languages available:
1. Optimizing Large-Scale Projects
Diagnosing and solving optimization issues in a large Scene requires the application of an optimization methodology, as well as a range of skills. This tutorial outlines a process to work through optimization issues in a coherent and structured way. Using this process will provide a consistent framework and approach to optimization that can be adopted across teams and embedded in your general optimization practices.
2. Optimization Process Overview
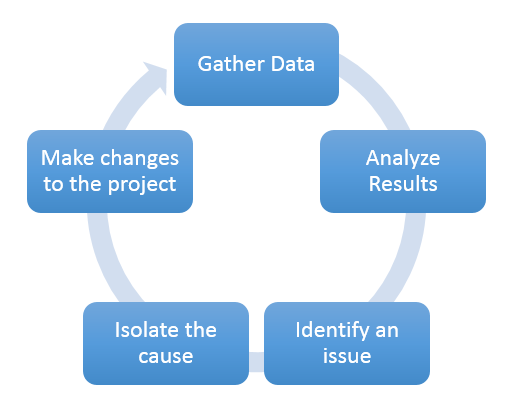
The optimization process follows a distinct, cyclical workflow with five areas of focus. This allows you to focus on, and resolve, one issue at a time before moving on to the next (Figure 01).
3. Gather Data
Use Unity’s suite of diagnostic tools to understand what’s happening in a game from a performance standpoint.
It’s extremely important to remember that when gathering data, it should be done on the target platform. Profiling on a high-end development PC may not make optimization issues as obvious.
4. Analyze Results
When analyzing data, the goal is to try to understand the root cause of the issue so you can address it properly. It’s always a great idea to figure out if your project is either CPU bound or GPU bound:
- CPU bound issues happen when there are too many tasks per frame. These issues are typically easily identified, but require more effort to correct.
- GPU bound issues arise when there’s a problem in the rendering pipeline, such as unoptimized lighting or an extreme amount of draw calls. GPU bound issues can be more difficult to identify, but can be easily fixed with the suite of tools Unity offers.
5. Identify an Issue
The analyzed results will present the full spectrum of issues occurring within the project. From this point, a single problem should be selected for closer inspection, using Unity’s diagnostic tool filters to separate it out from the others.
6. Isolate the Cause
Once a single issue is identified, the next step is to understand what’s causing it. The filters applied in the previous step will help identify the areas of the project to inspect, making it much easier to determine what needs to be optimized.
7. Make a Change
Once the issue has been identified, you need to make changes to the project. How you do this will depend on the specific problem, but could include actions such as refactoring scripts or reducing Texture size. While making a change, it’s important to stay focused on the issue and minimize the number of variables being affected at one time.
8. Repeat
Once the issue has been resolved, compare the changes and repeat the process as necessary.