Publishing for Android
Tutorial
intermediate
+10XP
30 mins
287
Unity Technologies
Unity includes a built-in publishing feature that allows you to publish to various popular platforms in an easy and efficient way. You can publish the same application to multiple platforms, provided the application design takes into account the unique hardware and software requirements of each platform. In this tutorial, we’ll explore publishing to Android-based devices.
Languages available:
1. Introduction
Unity includes a built-in publishing feature that allows you to publish to various popular platforms in an easy and efficient way. You can publish the same application to multiple platforms, provided the application design takes into account the unique hardware and software requirements of each platform. In this tutorial, we’ll explore publishing to Android-based devices.
For this tutorial, you will need:
- The Android Build Support module installed
- Updated Java SDK installed
- Android NDK and SDK installed
- A Pro license for the Unity Editor
- The Reflect package installed from the Package Manager.
2. Setting up your Environment
Before you can create Android apps with Unity, you need to prepare your development environment — specifically, you need an updated Java SDK, the Android SDK and NDK of the Android version you want to publish to.
You have two options with Unity: using the JDK and NDK versions installed with the Unity Hub or installing the official versions from the respective developers and then pointing Unity to those paths.
Using the hub installation is the fastest, and recommended, way to get up and running and is the option explored in this tutorial.
Note: Should you prefer to use the developer versions of the JDK, SDK, and NDK. You can download the latest Java SE JDK. The Android studio and alternative command line versions can be downloaded at https://developer.android.com/studio.
3. Installing with the Unity Hub
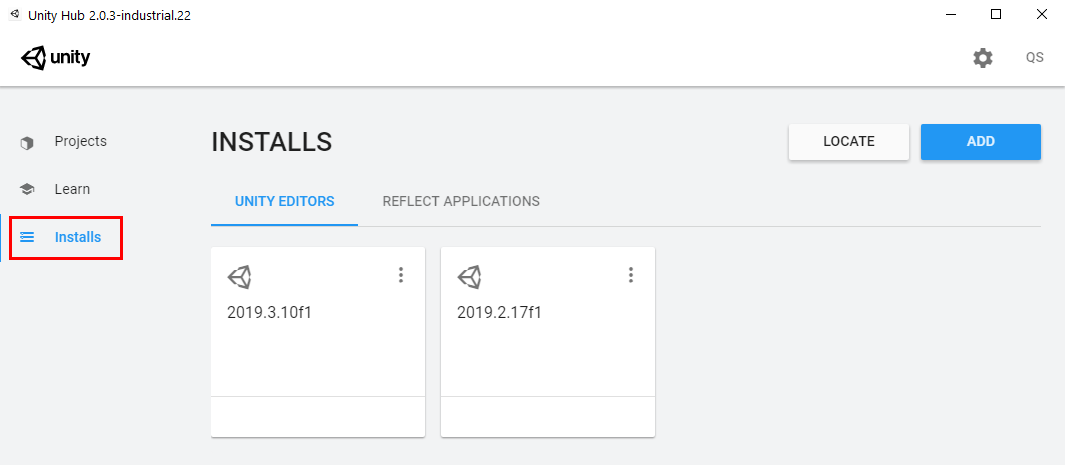
1. Open the Unity Hub and locate your installs (Figure 01).
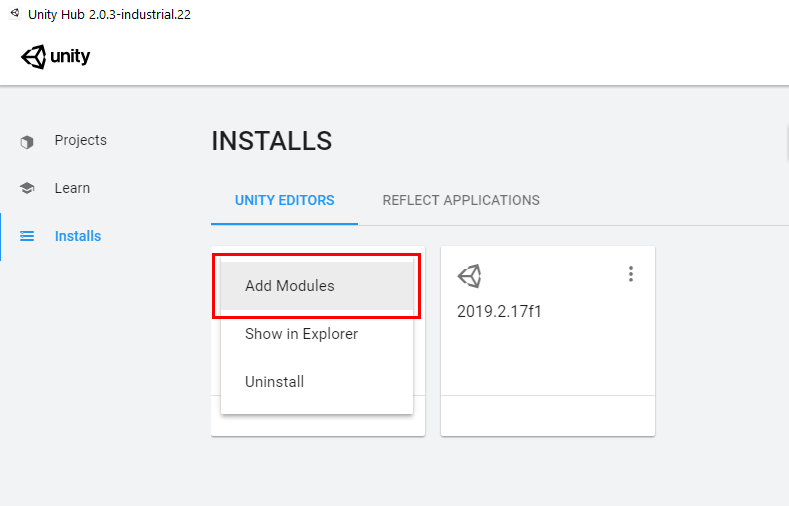
2. Select the three dots at the top-right corner of your working installation and select Add Modules (Figure 02).
3. Expand the Android Build Support section and select both the Android SDK & NDK Tools and OpenJDK (Figure 03).
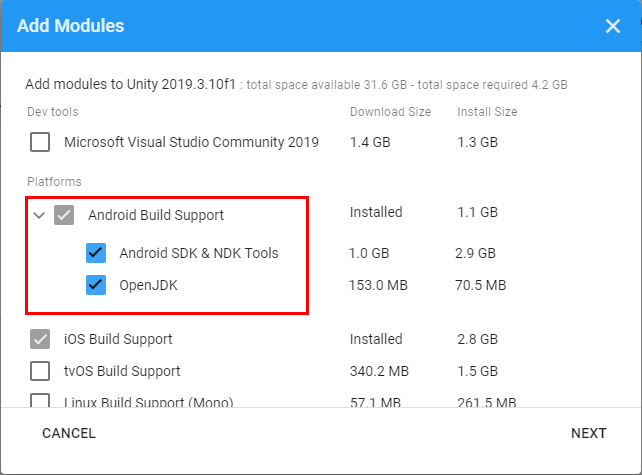
4. Click Next and accept the terms and conditions. Wait for the installation to finish.
5. In Unity, open your preferences by going to the menu bar at the top and selecting Edit > Preferences (Figure 04).
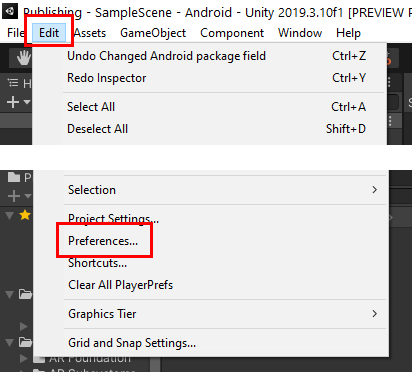
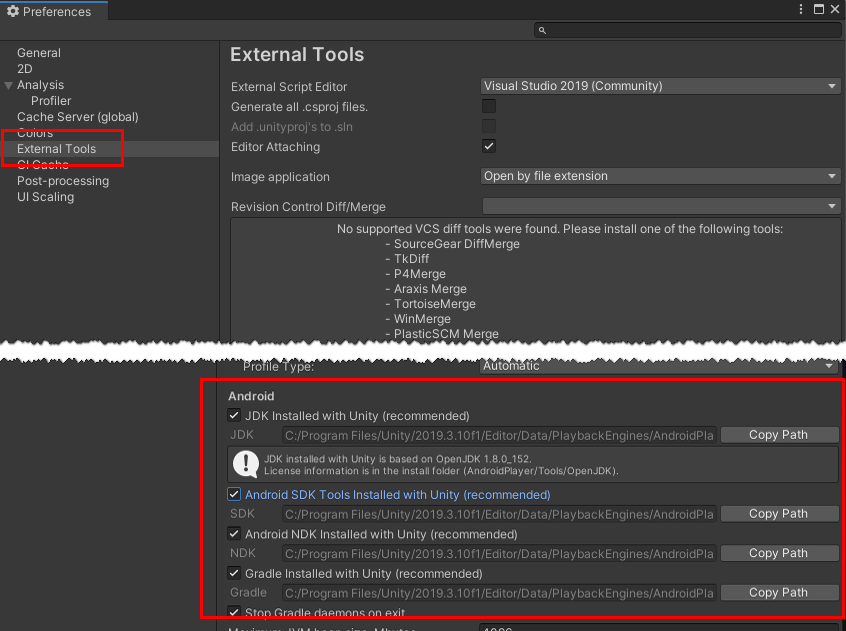
6. Select External Tools and make sure that the highlighted sections are set to use the tools installed with Unity by checking the relevant boxes (Figure 05).
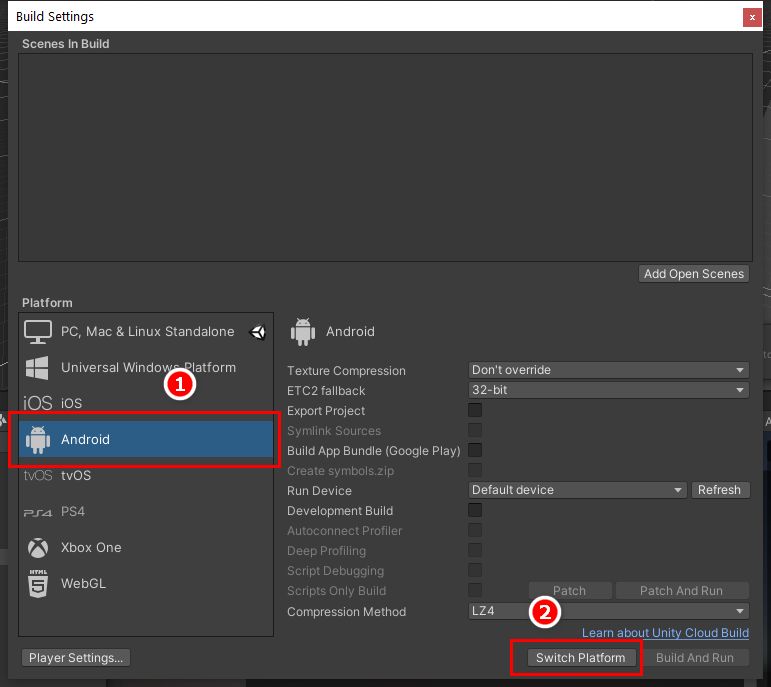
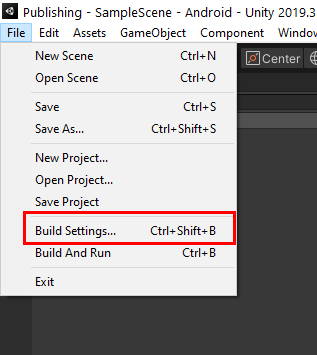
7. Go to the File menu and select Build Settings or press Ctrl-Shift-B to open the Build Settings menu (Figure 06).
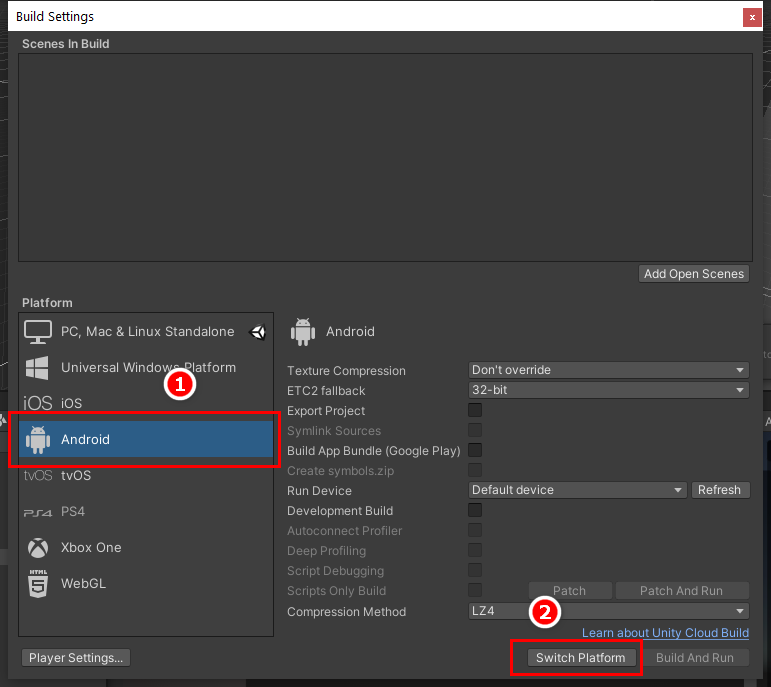
8. Select the Android platform and then select Switch Platform and wait for the required packages to install (Figure 07).
9. Select the Player Settings button on the bottom left (Figure 08).
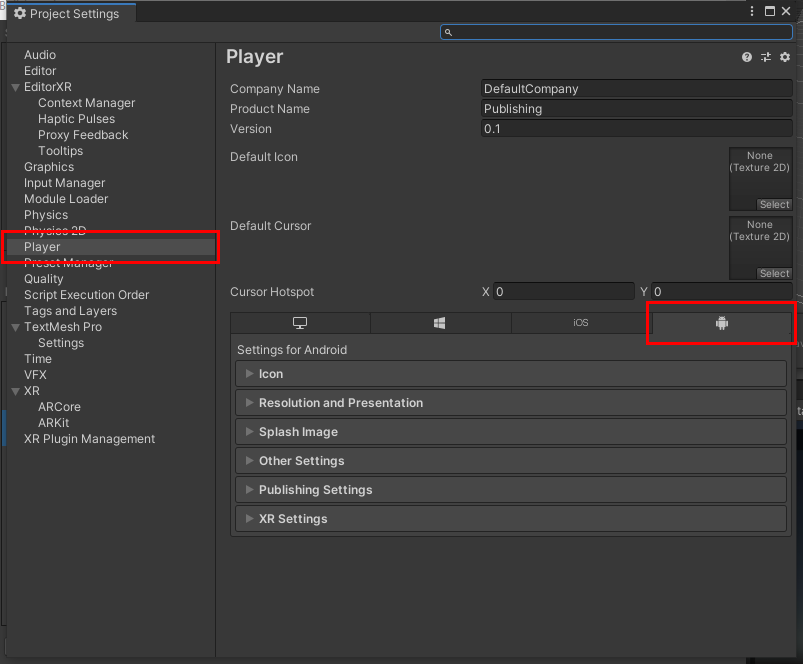
10. Make sure you have the Player Settings selected and that you are working in the Android tab (Figure 09).
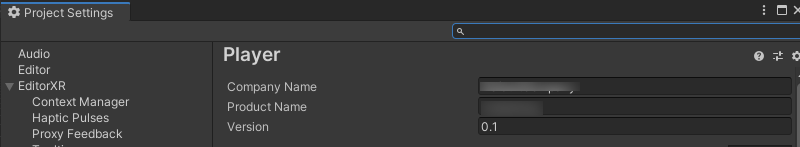
11. Enter your Company Name, Product (application) Name, and the Version number of the build (Figure 10).
12. The settings are separated into expandable sections:
a. Icon: This section allows you to set the icon of your app when you publish.
b. Resolution and Presentations: This section allows you to set the resolution of your game as well as behavior when a device is rotated between landscape and portrait orientations.
c. Splash Image: This section gives you access to all of the options that control the splash image of your app.
d. Other Settings: This section allows you to set the identification, performance, and graphic hardware settings of your application.
e. Publishing Settings: In this section, you can set values and requirements specific to the chosen publishing platforms.
f. XR Settings: If you are building virtual or augmented reality applications, this section allows you to activate the built-in technologies in Unity for your application.
The number of available settings can be overwhelming and can become complicated. Below, we’ll go through the typical minimum settings that you’ll need before publishing an Android app.
1. Leave the settings for Icon, Resolution and Presentation, and Splash Image on the default values.
2. Expand the Other Settings section.
3. Currently Vulcan graphics cause some problems with some Augmented Reality technologies. Remove it by selecting Vulcan and selecting the “-” option.
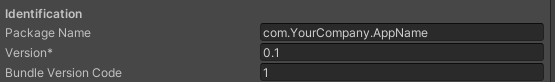
4. Change the Package Name by using a format of com.YourCompany.AppName (Figure 11).
5. Set the minimum API level you will be targeting. Generally, for AR, especially if you are using ARCore, you want to use Kitkat (Level 19) or higher. Set the Target API level to Automatic (highest Installed). This will look at the highest Android NDK on your system and create a package for that API level (Figure 12).

6. Expand the Publishing settings. Before an Android app can be distributed via app stores, it must be signed with a unique key (Figure 13).
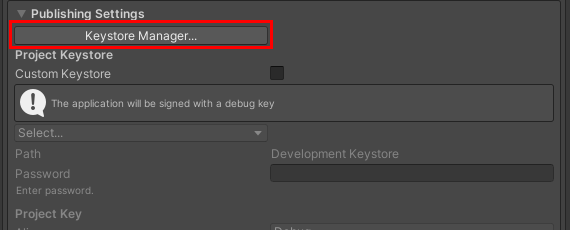
7. The Keystore is where all of your generated keys are stored. For this tutorial, you will create a new key for the application. Select the Keystore Manager.
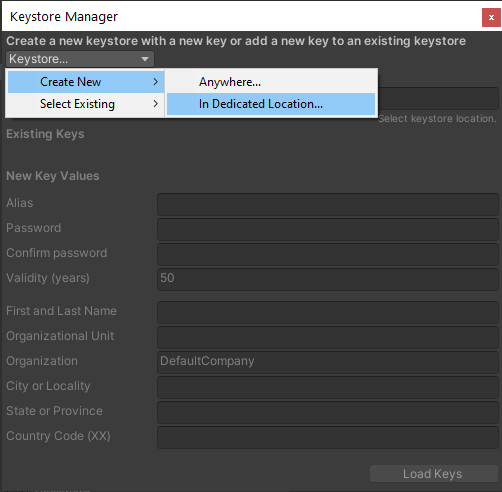
8. Select the Keystore button at the top left of the Manager window. In the drop-down menu, select Create New and then In Dedicated Location. It’s a good idea to keep your keys in a separate secure location. Select a location where the file will be saved (Figure 14).
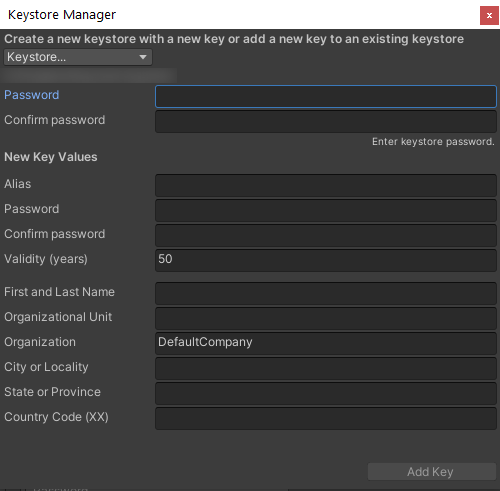
9. Fill out the required information. The maximum validity for a key is 1,000 years. In this case we will use 50 years but this is up to you. Select a secure password you will remember. Should you forget the password, you will have to generate a new key and re-publish the application. Select Add Key at the bottom right to create the new key (Figure 15).
10. Close the Player Settings window.
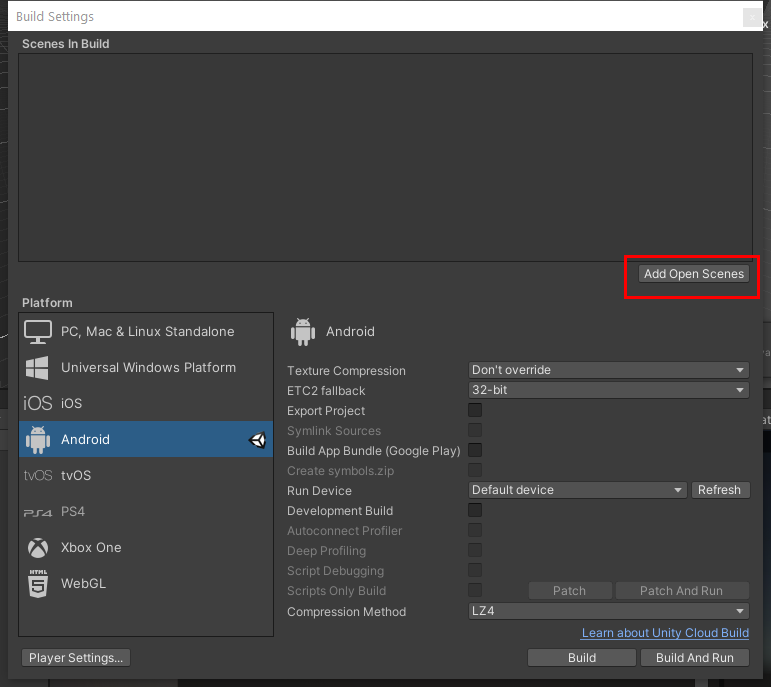
11. The final step before publishing is to add a Scene to the Build Settings. This will be the Scene that will open first when the application runs. Select the Add Open Scene button to add the current open Scene to the application build (Figure 16).
12. Select Build to create the .apk file. This file can be copied to your device for testing and submission. Uploading your .apk file to the application marketplace and setting up a store page is beyond the scope of this tutorial. Please consult resources from the official publishers for more information on this process.
4. Next Steps
You now have a publishing environment set up to generate Android APK files. You can now create builds of the same application for other platforms or go to the Android-based stores you want to publish to and upload your new .apk file using their specific processes and requirements.